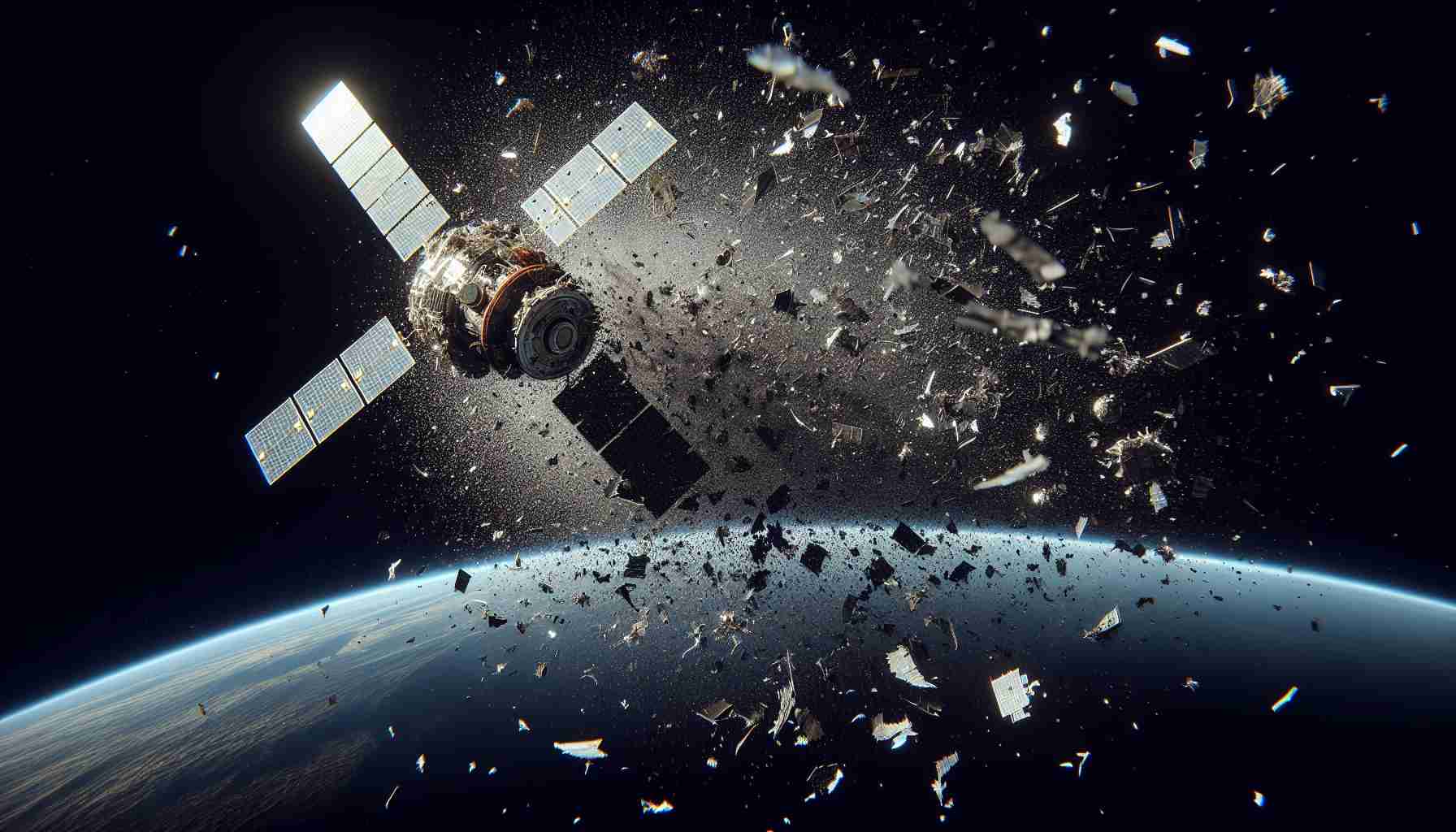
A secret Russian satellite experienced a catastrophic failure, leading to the fragmentation of the spacecraft and the creation of a cloud of debris in Earth’s geostationary orbit. The incident marks the second time a satellite has broken apart in this region, raising concerns about the escalating risks of collisions in space.
The ill-fated Russian satellite, whose mission and purpose remain undisclosed, suffered a critical malfunction that resulted in its disintegration into multiple fragments. This unexpected event has significantly contributed to the growing clutter of space debris, heightening the potential for collisions with operational spacecraft and posing a threat to the safety and sustainability of satellite operations in geostationary orbit.
Observers and experts, including astrophysicists and space agencies, have expressed alarm at the increasing frequency of satellite breakup events in this crucial orbital region. The challenges posed by the accumulation of debris in geostationary orbit underscore the urgent need for enhanced space debris mitigation strategies and responsible satellite deployment practices.
While the specific cause of the Russian satellite’s failure remains unknown, the incident serves as a stark reminder of the complex and unforgiving environment of outer space. As the number of satellites and orbital debris continues to rise, international cooperation and regulatory measures must be prioritized to ensure the long-term sustainability of space activities and safeguard vital communication and navigation services for future generations.
Uncovering Additional Details of the Russian Satellite Failure and Space Debris Consequences
Following the recent catastrophic failure of a secretive Russian satellite that resulted in the fragmentation of the spacecraft and the dispersal of debris in geostationary orbit, new insights have emerged regarding this concerning incident. As the space community grapples with the implications of this event, several crucial questions arise along with key challenges and advantages associated with managing space debris and ensuring the safety of future satellite operations.
Important Questions:
1. What is the estimated amount of debris generated by the Russian satellite failure, and how does it compare to previous space debris events?
2. How are space agencies coordinating efforts to track and monitor the movement of the debris cloud to prevent potential collisions with other spacecraft?
3. What measures can be implemented to mitigate the risks posed by the growing accumulation of space debris in geostationary orbit?
Answers and Key Challenges:
1. The Russian satellite failure is estimated to have produced hundreds of fragments, adding significantly to the existing debris population in geostationary orbit. This incident highlights the pressing need for better space situational awareness and debris tracking capabilities to assess the impact on operational satellites.
2. Space agencies such as NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) are collaborating to track the trajectory of the debris cloud and provide timely collision predictions to satellite operators. However, the sheer volume of debris and the complexity of orbital dynamics present challenges in accurately predicting debris movements.
3. Mitigating the risks associated with space debris requires a multi-faceted approach, including enhanced debris removal technologies, stricter regulations on satellite design for post-mission disposal, and international cooperation to establish guidelines for responsible space operations.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
– Advantages: Increased awareness of the hazards of space debris can spur innovation in debris mitigation technologies and promote greater transparency in satellite operations. Collaborative efforts among spacefaring nations can lead to more effective strategies for managing and reducing space debris.
– Disadvantages: The presence of debris in geostationary orbit poses an ongoing threat to operational satellites and could potentially limit the future expansion of satellite-based services. Addressing the challenges of space debris mitigation requires significant investments and regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance across the aerospace industry.
As the space debris environment continues to evolve, it is imperative for stakeholders to prioritize sustainable space practices and implement proactive measures to safeguard critical orbital assets. By addressing the complexities of space debris management, the global space community can mitigate risks, preserve orbital ecosystems, and uphold the long-term viability of space exploration and satellite technologies.
For further information on space debris monitoring and mitigation efforts, visit NASA’s official website.