


October 8, 2025
Niagara Falls Real Estate 2025: Cross-Border Boom, Surging Tourism & Future Forecasts

October 7, 2025
Is the Global Real Estate Slump Finally Over? Mega-Deals and New Forecasts Signal a Turnaround






October 4, 2025
Winnipeg Real Estate Market 2025: Prices Skyrocket Amid New Housing Boom – What’s Next?


October 3, 2025
Saskatoon Real Estate 2025: Record Prices, Skyrocketing Sales and a Market on Fire – What’s Next?

October 3, 2025
Real Estate Rollercoaster: Mortgage Rates Plunge, Home Sales Surge, China Prices Crash – Global Market Update (Oct 2025)
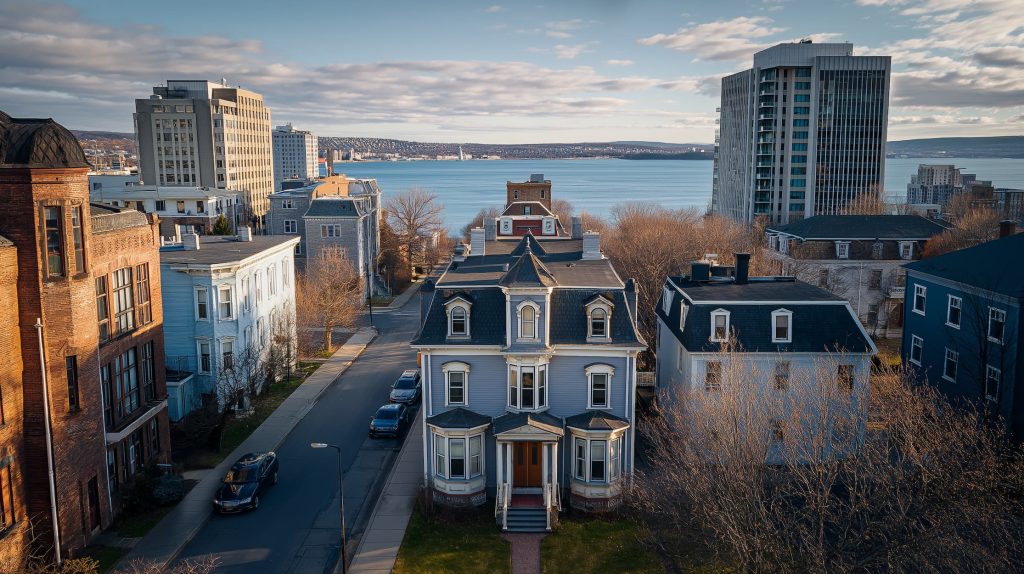
October 2, 2025
Halifax Real Estate Market 2025: Surprising Price Trends & Top Investment Opportunities

October 2, 2025
Global Real Estate Rollercoaster: Dubai Surges 60%, Saudi Opens Market & US Rental Lawsuit

October 1, 2025
Vancouver Island Real Estate 2025: Boom or Bust? Surprising Forecast & Key Trends Revealed

October 1, 2025
Global Real Estate Frenzy: Surging Home Prices, Tech Showdowns & $Billions in Deals (Sept 30 – Oct 1, 2025)

September 30, 2025
Victoria’s 2025 Property Market Set to Explode: Prices, Hotspots & Expert Forecasts

September 30, 2025
Global Real Estate Rollercoaster: US Home Sales Jump, Asia Deals Surge, Europe Stalls – Global Market Update (Sep 29–30, 2025)

September 29, 2025
Québec City Real Estate Market Explodes in 2025: Record Prices, Frenzied Sales & Future Forecasts

September 29, 2025
Global Real Estate Rollercoaster: Interest Rate Cuts Spark Housing Rally Amid Mega-Deals

September 28, 2025